Manage¶
The “Manage” entry in the Burger menu adjusts global configurations.
Locations¶
Here you can manage the locations and create new ones.
Furthermore, the column with the heading “Connected” allows you to filter for locations that already communicate with the ResMa®
Change setpoints globally¶
Use the Change Setpoints Globally button to change setpoints from multiple offices at the same time. You can use the column filters to filter out the branches whose setpoints you do not want to change.
Apply selection to pivot¶
With the “Apply selection to pivot” button, you can transfer the current selection of branches to the pivot for further data analysis. All branches that are not filtered out are transferred to the pivot.
Run analysis¶
The Run Analysis button allows you to run an analysis rule on the branch offices that are currently being viewed. You can use the column filters to filter out the branches that you do not want the analysis rule to check.
Manual input¶
With the manual input function, values of individual measuring points can be manually e.g. the recording of laboratory values.
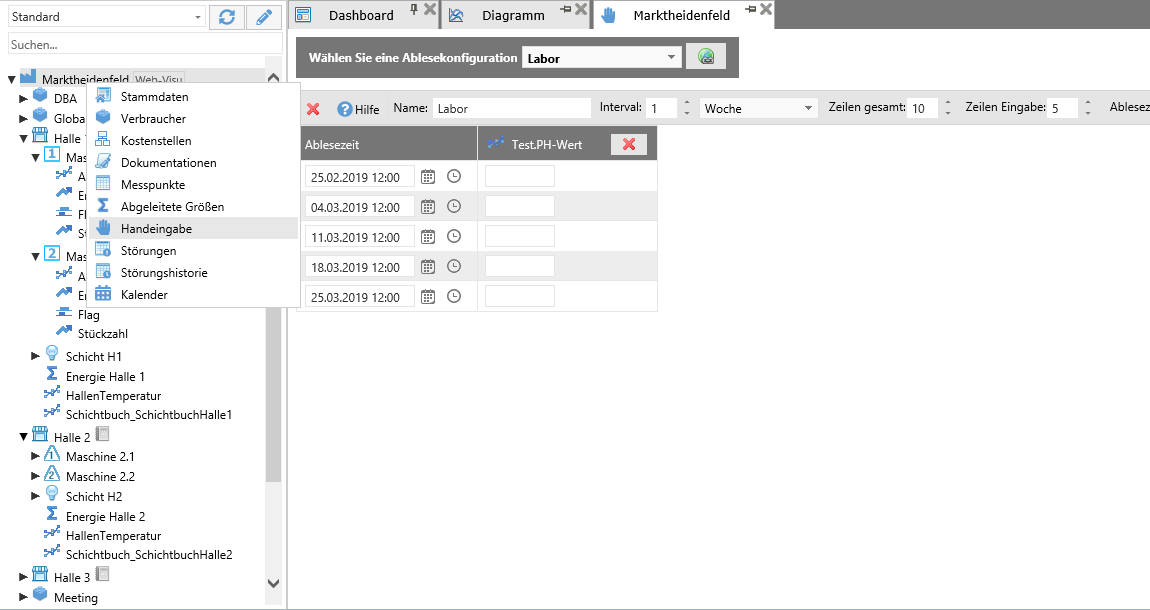
Open Manual Input¶
The manual input is called up via the context menu of the branch office or via the menu “Administration”.
Configuration Manual Input¶
For a new manual input, a new configuration is first created after calling up the page.
Any values can then be dragged and dropped from the object tree into the manual input.
Finally, an interval for data collection is set and the configuration is saved.
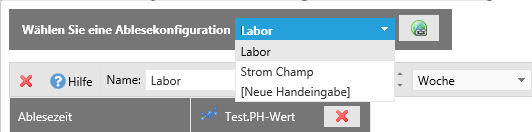
Consider the following:
The Total Rows value is the maximum possible value of the display, depending on how much data has already been entered for the measuring pointwere, see example
The value for “Row Input” is also to be understood as the maximum value, depending on the interval set, since the input fields never display the exceed current date
Entering values¶
The manual entry of values is carried out with plausibility check
For counter:
Consumer and counter values can be entered
New value greater than old value (for counters)
Consumption similar to the previous period (converted to
For real values:
Input between min and max value
Input is similar to the previous input
Furthermore, when the values are saved, the factor taken into account. However, this only applies to the input, not to the display.
Documentation¶
Documentation can be created from the APPs at various points in ResMa®. They serve to record discrepancies or findings for oneself and others. All documentation can be viewed in this table. If there are comments for a documentation, an icon appears in the first cell with which you can expand the line and read the comments on the documentation. The symbol of the first column indicates whether the documentation has been completed or is still active.
If a view has been saved with the documentation you can display it with the “Show saved view” button
Calendar¶
Here you can edit a new or existing appointment. If the editing is done via a dialog, the changes must be confirmed with “Save”. If the calendar is opened via the “Administration”, only the global appointments can be seen. If the calendar is called via an object, the global and object-specific appointments can be seen.
New appointment¶
A new appointment can be created via the context menu in the scheduler. The appointment requires a name and can contain a description. Furthermore, a category is assigned as well as the start and end time is defined.
Edit appointment¶
There are several ways to edit an appointment:
From the context menu in the scheduler
By double-clicking on an appointment
By moving the appointment in the scheduler
By zooming in/out in the scheduler
Delete appointment¶
There are two ways to delete an appointment. On the one hand via the context menu in the scheduler. On the other hand, directly via the “X” in the upper right corner of the appointment when the cursor is over the appointment.
Category¶
By default, there are 5 categories (maintenance, production, special day, holiday, company holidays) that cannot be deleted. It is only possible to edit the color. However, you can create additional categories and edit/delete them. Furthermore, you can hide appointments in the scheduler by selecting/deselecting the category via the checkbox.
Tariffs¶
Here you can manage the tariffs and create new ones.
Edit tariffs¶
In this view, a plan can be created or edited. The view is divided into three areas.
In the upper part you enter the “header data” of a tariff. To save the plan, you must enter a name. Furthermore, you can optionally enter a comment, the contract number, the provider or the medium. There is also the option to limit the validity.
In the middle area you can give more details of the tariff. Here it is possible to limit the tariff in the season, the day of the week and the time of day. In addition, a price can be indicated. If the tariff contains different types, you can create additional tabs to enter the values.
In the lower area you can define assignments to branches. In the left combo box there is the choice according to which criterion the assignment should be made. According to the selection, the possible branches are offered in the right combo box. Now an assignment can be made by ticking the checkboxes.
After entries have been made, they must be confirmed with “Save”.
Orders¶
In this view, orders can be viewed and managed. After an order has been entered, the statistics for the order can be called up via the button at the end of the line.
Orders are either entered manually, imported through external data sources or automatically recorded by ResMa® via measured values. If you need additional attributes on jobs, you can use Custom Attributes in the System tab to add additional attributes.
Notification Templates¶
Templates can be created in this view, with which it is possible to influence the text of a alert forwarding. These templates are later assigned to maintenance providers.
Edit Templates¶
In this view, a template for alert forwarding can be created or edited. In addition to the name of the template, the subject text of the e-mail, the e-mail text, as well as an SMS text must be determined. With the help of placeholders, variable text (such as .B alert number, alert text, branch name) can be added. Placeholders can be used in both the subject line and the text. Furthermore, it is possible to send the interference forwarding e-mail in HTML format. If the content of the SMS is to be identical to that of the e-mail, this can be specified with the help of the check box “Copy SMS text from e-mail text”. It should be mentioned that mobile phones do not support HTML.
The placeholders %QuitNumber% and %QuitNote% are replaced by an empty text, no acknowledgement is required. Similarly, the placeholder %CurrentValues% is replaced with an empty text if this information is not present.
Data Analysis Rules¶
The data analysis rules can be used to carry out automatic checks of the energy data (e.B. detection of consumption peaks). In the menu item “Data analysis rules” all rules are listed. There are two general rules, further rules can be integrated at the customer’s request or entered via SQL scripts.
Query for an automatic scan¶
The link in the Run column can be used to evaluate a rule, the current execution progress, or the execution result.
The calendar selector selects the start and end time at which a rule should be queried.
Authenticated users can use a database procedure to add rules or modify existing rules.
When a rule is executed, load profiles of all branches are checked in a specified period of time and displayed in the form of a list.
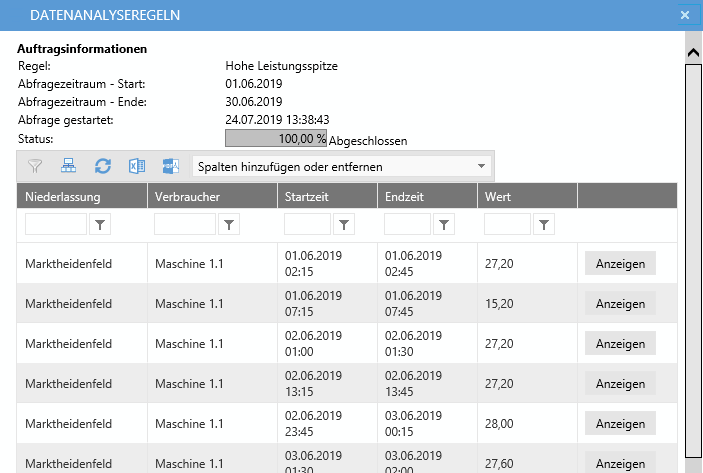
Creating a Rule¶
In this view, a rule can be created or modified. In addition to the name and description, a procedure name must be assigned. This procedure is called when it is executed. if you want the rules to run cyclically an interval must be selected under automatic validation.
An alarm must then be selected that is triggered in the event of a rule break. Finally, any number of parameters can be added. These are entered by the user before they are executed and then passed on to the procedure. For parameters, a unit can be specified in addition to name and description, which is displayed during the parameter query.
Executing a Rule¶
In this view, you start a rule check. To do this, specify the time period to be checked and the parameter values. After you confirm that the rule is started, all performance data of all branches at the specified time period is checked.
Execution Result List¶
This view displays the current execution progress or the result of the rule execution. All results are listed under the progress bar. The Show button can be used to open the rule break chart. You can stop the execution at any time with the “Cancel” button and return to the overview. During the execution it is possible to leave this page and return later.
Exceeding maximum values¶
With the rule “Maximum value exceedance” it is possible to determine a limit value exceedance for all values and to define the maximum value and the duration of the exceedance.
If automatic execution is disabled, the query must be started manually, otherwise the scan will be performed automatically at this time interval.
In the case of automatic execution, an alarm can be assigned, which is automatically triggered if the rule is exceeded.
In the overview table of the energy monitor, the “Start Query” link can be used to start the rule manually.
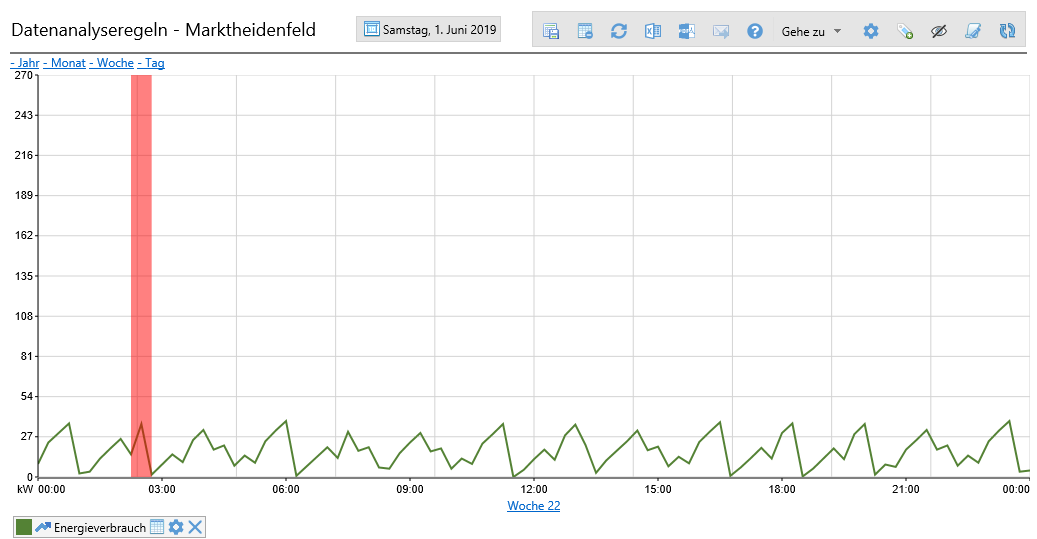
After selecting the time range, the evaluation is started and then the rule exceedances are displayed in a list. If an evaluation is then selected, the diagram of the respective time is opened.
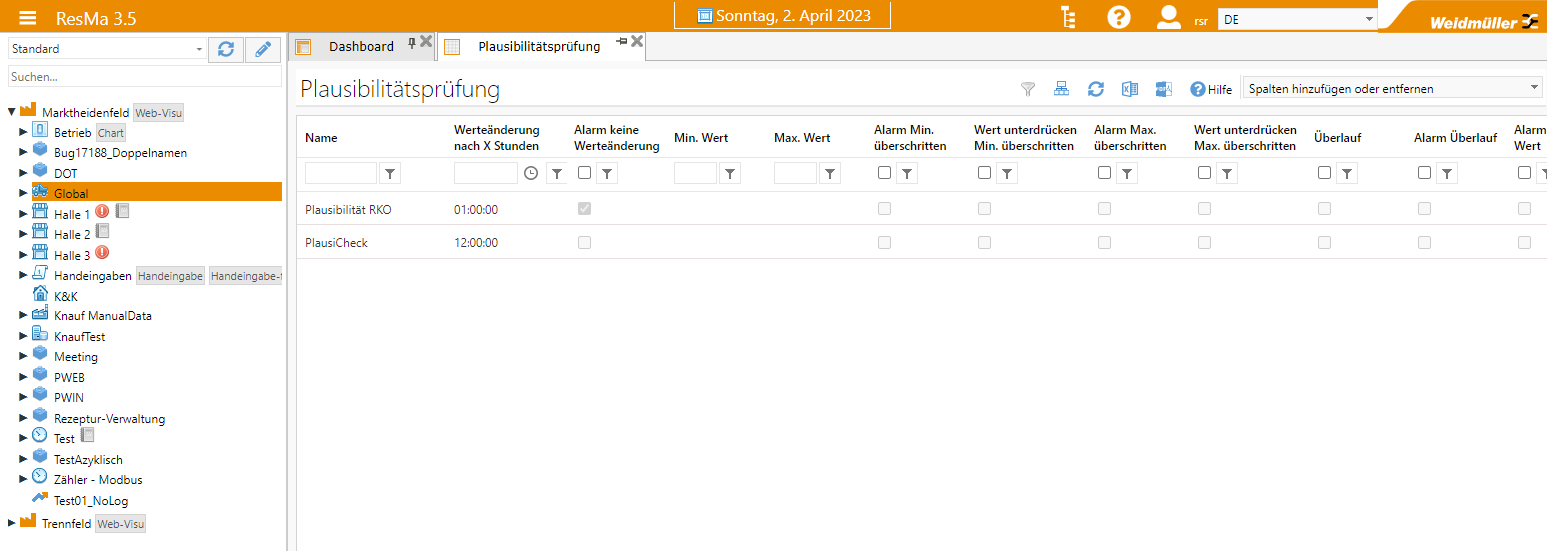
Validity check¶
Opens a tab with a list of all created plausibility checks.
The plausibility checks can be created and edited here, and later selected for a measuring point.
Measuring point monitors¶
Opens a tab with a list of all created measurement point monitors. The measuring point monitors is created or edited in the master data of measuring points.The measuring point monitor is only available for measuring points that are are connected via connector logging.
Measurement copier¶
Opens a tab with a list of all created copiers. The measured value copier is created or edited in the master data of measuring points.
Automatic export¶
Opens a tab with a list of all created automatic forwardings or automatic exports. The automatic exports created or edited in the various evaluation apps.
Resources / Greenhouse gases / Validity start point¶
The structure from the meter to the validity start point is shown here.
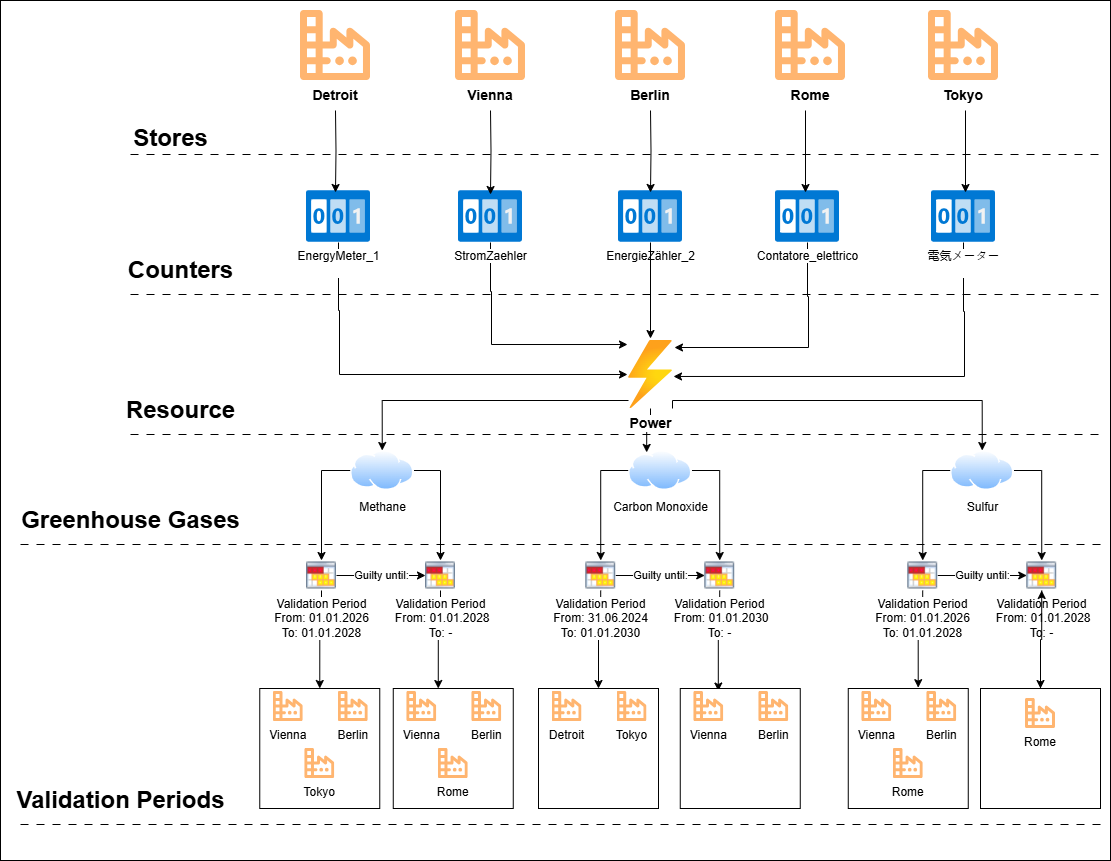
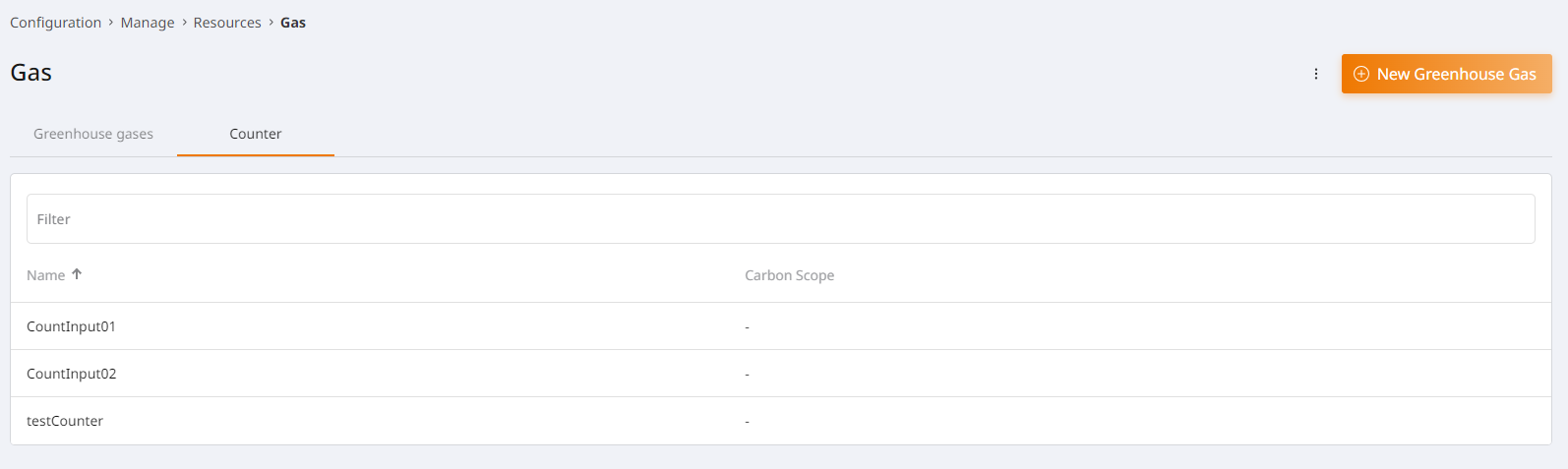
Ressources¶
Opens a tab with a list of all created resources. Here you can new resources can be created, edited and deleted. Additionally the number of meters allocated and greenhouse gases displayed. With a mouse-over over the info icons, a tooltip which displays a list of meter/greenhouse gas names.
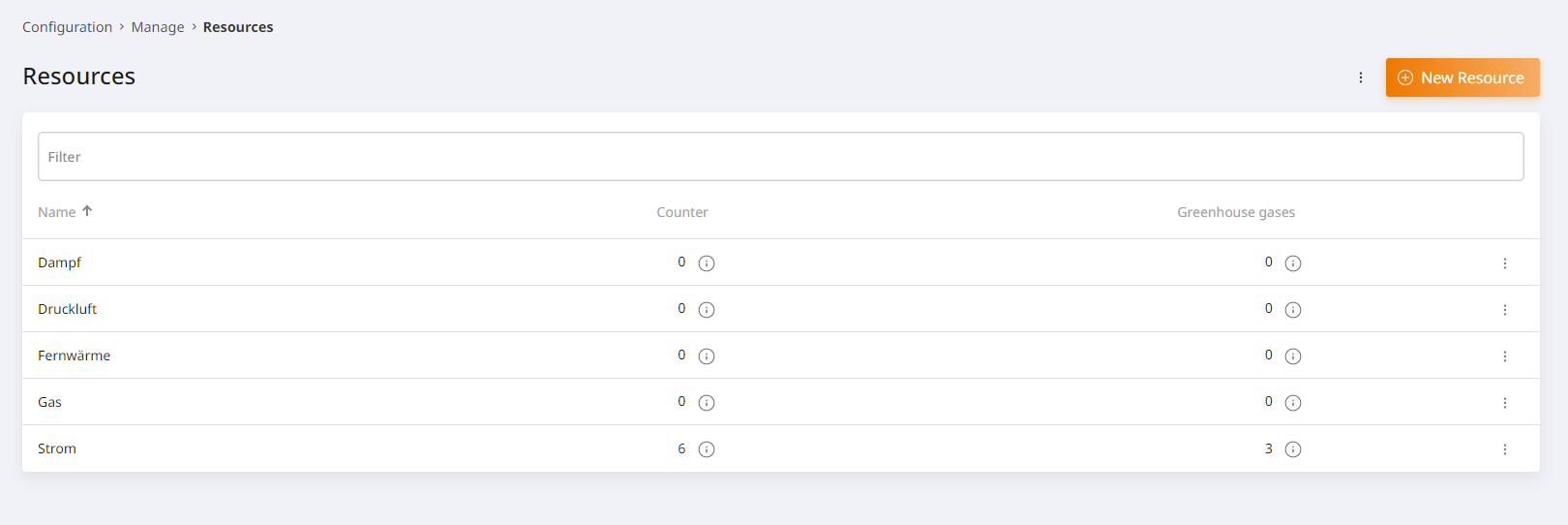
The resources of the type “counter” are used and allocated at the measuring point.
Ressources detail page¶
When you click on a resource, the detail page is opened. This displays as a default view a list of all greenhouse gases that are behind of the resource itself. This is where new greenhouse gases can be created/edited or deleted. Will a greenhouse gas expanded, the corresponding validity start points are listed.
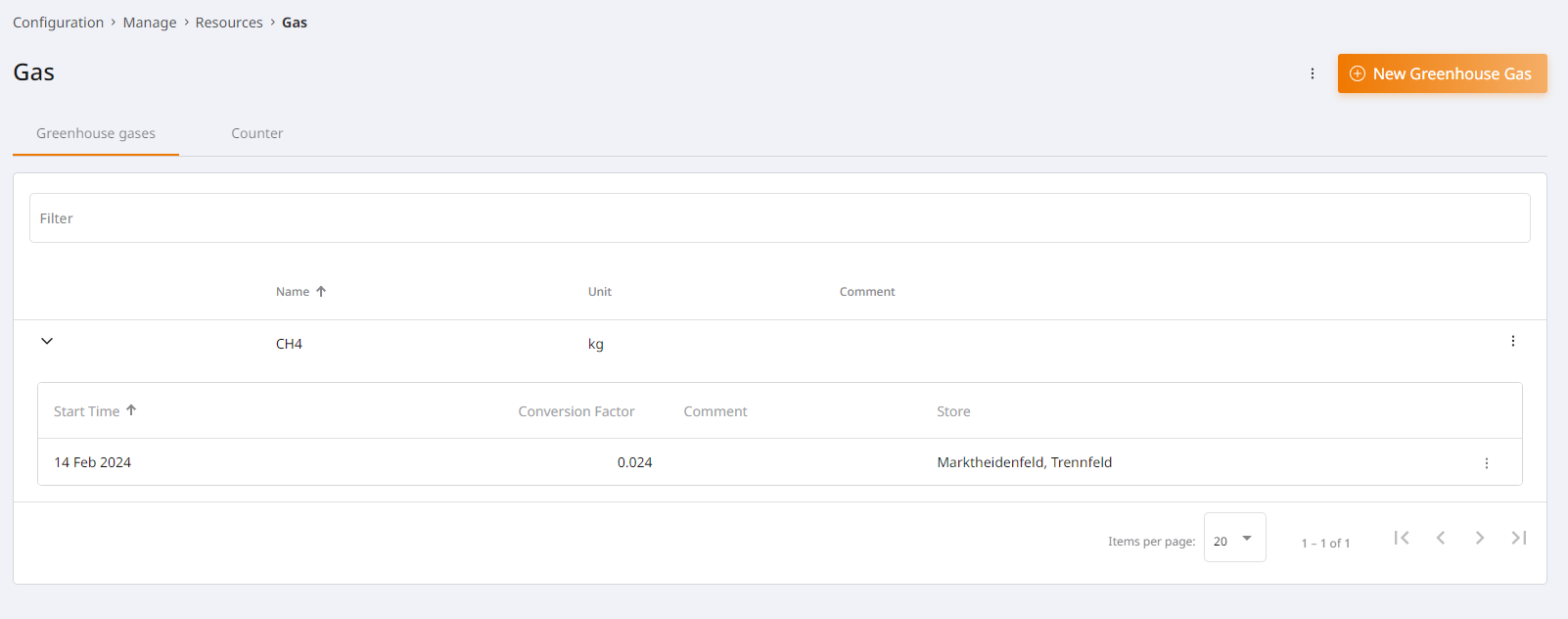
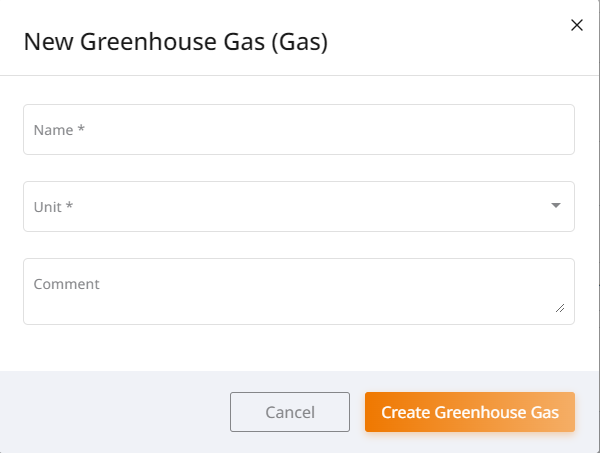
Greenhouse gases¶
A greenhouse gas consists of a name, a unit and, if applicable, a Comment and is used to calculate greenhouse gas emissions (carbon)Footprint). Editing, extinguishing a greenhouse gas is done via the 3-dot menu at the end of the line. The creation of a new greenhouse gas is done via the button “New greenhouse gas”, which opens a dialog Window opens. When creating a greenhouse gas, it is important to note that Name/unit are required.
Validity start point¶
Validity start points are an essential component for calculating greenhouse gas emissions. They determine the conversion factor for a greenhouse gas and the period during which it is valid. A new validity start point can be added either via the “Add validity start point” button (only for empty greenhouse gases) or via the 3-dot menu at the end of the greenhouse gas line. Deletion and editing are performed via the 3-dot menu at the end of the line. The validity start point is valid until a new start point begins. Likewise, only one validity start point per greenhouse gas can be active per branch at any given time

Formula of the CO2-Equivalent (conversion factor)¶
The conversion factor affected by 2 factors.
- The amount of the exhausted greenhouse gas per counter unit
Example: Per 1kw/h of a power meter, 2 tons of Methan are released
- The greenhouse gas potential GWP (Global Warming Potential), which is determined by the IPCC (Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change).
Example: The GWP for Methan is 28
- Default fomula of the conversion factor:
Amount of the greenhouse gas x GWP = CO2-Equivalent (conversion factor)
- Formula with the sample data of Methan:
2 tons x 28 GWP = 56 tons CO2
Therefore, the conversion factor of this example: 56
Ressources detail page (counter)¶
Under the “Counter” tab in the resource detail page, you get oneListing of all counters that have been assigned to the current resource.